Cellular technology enables reliable and efficient communication between doctors, nurses, caregivers, and support staff, and delivers patients and guests an elevated experience.
What is a Distributed Antenna System?
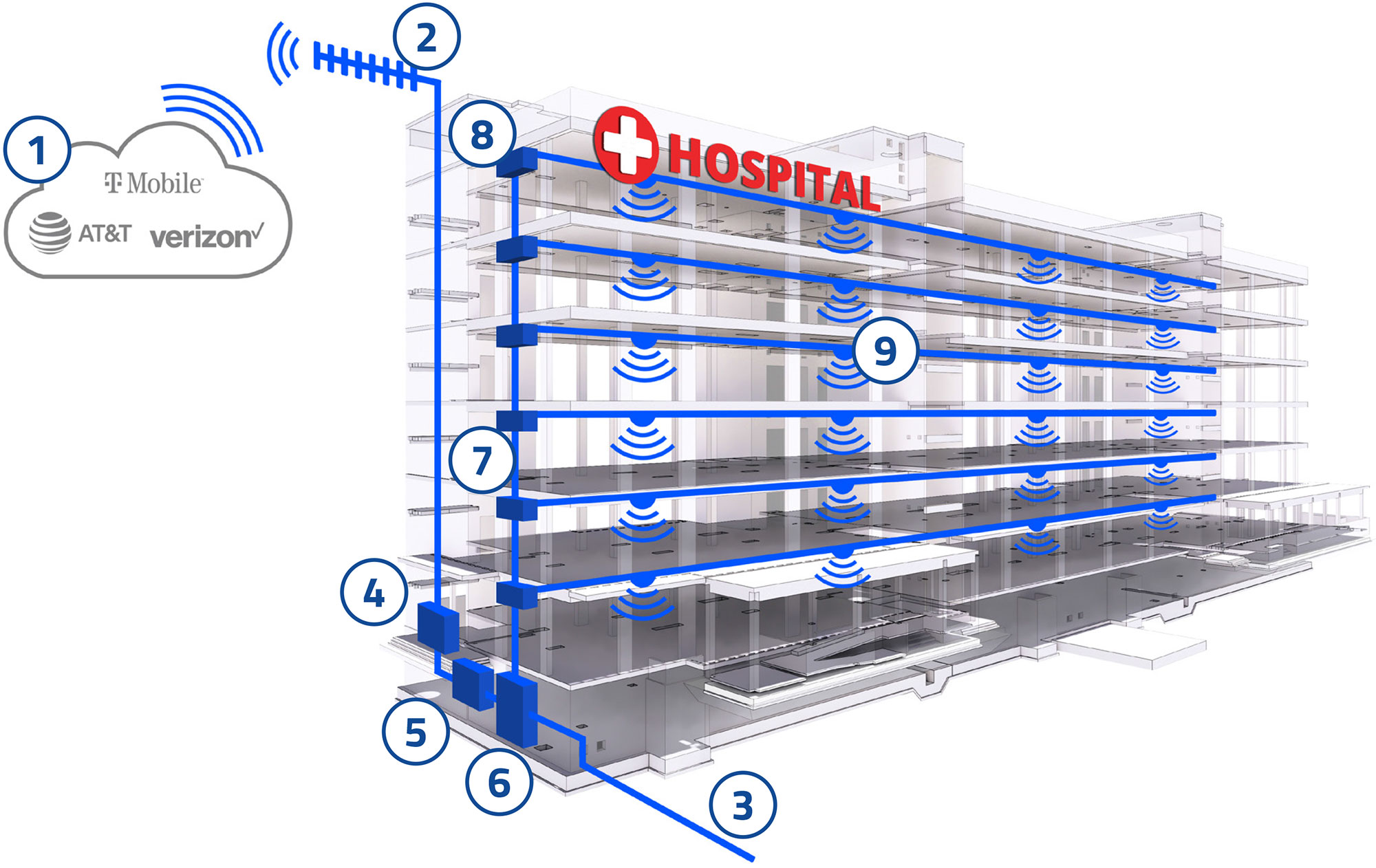
Put simply, a distributed antenna system (DAS) is a wireless solution that provides reliable cellular communication within a defined space.
More specifically, a DAS is a network of spatially-separated antennas connected to a common signal source and distributed throughout a defined coverage area to support and enhance the transmission of public cellar network signals.
What are the Benefits of In-Building Cellular Enhancement?
Modern healthcare embraces an undeniable fact – technology positively impacts lives.
Occupying a position at the forefront of healthcare technology is Cellular. Cellular (or Mobile) technology enables reliable and efficient communication between doctors, nurses, caregivers, and support staff, assisting in the delivery of key patient services. It provides a wireless backbone for user-device-based communications applications, medical equipment, IoT devices, and essential points of interface for healthcare staff and administrators.
Cellular also plays a key role in the patient and guest experience with a healthcare facility, as each expects a flawless interaction with their favorite wireless devices to communicate with loved ones, stream video, or otherwise remain educated and entertained during their stay.
Healthcare facilities, and in particular, hospitals, present some of the most challenging scenarios for cellular networks. Many older buildings’ designs include lead-lined rooms and tiled walls, environments that work against wide-ranging radiofrequency (RF) coverage.
Newer building construction includes a preponderance of steel, concrete, and low-emissivity (Low-E) glass, which creates a different set of challenges for a reliable cellular signal in large hospitals or multiple-level clinics.
Simply put, the density of materials, coupled with the square footage within a healthcare structure make it difficult for outside cellular signals to penetrate and populate the entirety of the space.
Telecommunications industry analysts state as much as 80% of all cellular network demand occurs inside buildings and structures, and demand and data consumption will continue to increase exponentially as (1) carriers roll out 5G coverage and (2) innovators tap into the additional bandwidth and speed made available by the generation advancement in the network.
For healthcare venue facing these challenges, a distributed antenna system, or DAS, is the perfect solution to extend public cellular network coverage and connectivity into all areas of your property. Eliminating dropped calls and increasing the speed and capacity of the network experience will result in higher productivity and greater user satisfaction by those onsite.
How Does a DAS Work?
Every DAS has two key elements – a signal source and a distribution system. There are three kinds of signal sources that receive cellular signals from mobile carriers, and they are (1) off-air antennas, (2) on-site base transceiver stations (BTS), and (3) small cells. Once the signal is secured from the carrier, it is distributed throughout the environment via different types of solutions, notably active, passive, small cell, or picocell distribution systems.
The choice of distribution system is driven by a number of factors:
- How big is the coverage area?
- How many devices and users are expected to utilize the enhanced cellular network (commonly referred to as density)?
- What mobile carriers do you need (AT&T, Dish, T-Mobile, US Cellular, Verizon, regional carriers)?
- What is the performance goal of the enhanced network? Does the DAS need to solve for issues like capacity, frequently dropped calls, and/or speed and latency issues?
Pierson Wireless can guide you through an analysis of these factors to determine which distribution system best fits your use case.
Our Healthcare Partnerships













Our Healthcare Partnerships

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|